Q) An infant presents with duodenal atresia. Which of the following is true about this condition?
a) It is the most common GI atresia
b) It presents soon after birth with non bilious vomiting
c) Pre natal detection of duodenal atresia is common
d) Gastro jejunostomy is the procedure of choice to bypass the obstruction
Understanding Duodenal Atresia in Infants: Key Facts and Diagnostic Insights
Duodenal atresia is a congenital condition that affects newborns, impacting their gastrointestinal (GI) system. While not the most common form of GI atresia, it is a significant condition that requires early detection and treatment. This article delves into the critical aspects of duodenal atresia, including its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
What is Duodenal Atresia?
Duodenal atresia is a congenital obstruction of the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine. This condition occurs in approximately 1 in 5,000 live births and is associated with other congenital malformations, such as Down syndrome, prematurity, and biliary atresia.
Prenatal Detection of Duodenal Atresia
Early Diagnosis through Ultrasound
One of the most notable aspects of duodenal atresia is that it is commonly detected during prenatal ultrasounds. Advances in antenatal sonography allow doctors to identify most cases before birth, providing an opportunity for early planning and intervention. The typical sign on ultrasound is a "double bubble" appearance, which indicates the presence of fluid-filled areas in both the stomach and duodenum.
Symptoms and Presentation
Bilious Vomiting After Birth
Duodenal atresia typically presents soon after birth, with one of the hallmark symptoms being bilious vomiting. In around 80% of cases, the obstruction is located distal to the ampulla of Vater, allowing bile from the liver to mix with stomach contents, leading to greenish, bilious emesis.
Associated Congenital Conditions
Infants with duodenal atresia may also present with other congenital anomalies, such as Down syndrome, heart defects, or other gastrointestinal malformations like jejunoileal atresia, which is actually the most common type of GI atresia (occurring in 1 in 2,000 live births).
Types of Duodenal Obstructions
Stages of Duodenal Atresia
Duodenal atresia can occur in various forms, ranging from partial obstruction, such as duodenal webs, to complete separation of the duodenum. These different forms dictate the severity of symptoms and the urgency of intervention.
- Duodenal Webs – Thin membranes that partially block the duodenum.
- Stenosis – A narrowing of the duodenum that restricts food passage.
- Complete Atresia – A total obstruction where the duodenum is completely separated.
Diagnostic Features
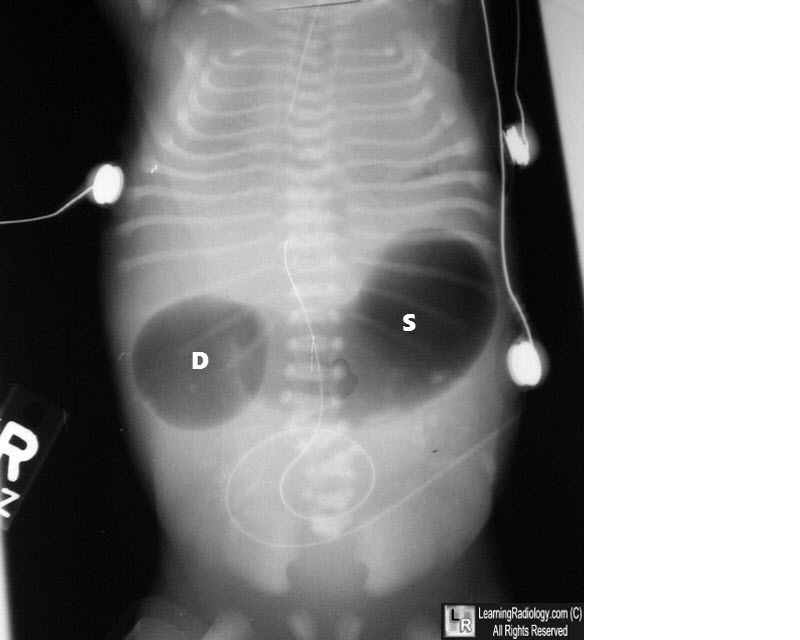
Double Bubble Sign on Imaging
Postnatally, duodenal atresia is diagnosed through abdominal imaging, with the "double bubble" sign being a classic radiographic finding. This sign appears as two distinct gas-filled bubbles—one in the stomach and one in the duodenum—indicating the obstruction.
Treatment of Duodenal Atresia
Surgical Intervention
The treatment for duodenal atresia is surgical, with the goal of bypassing or removing the obstruction. Contrary to some misconceptions, gastrojejunostomy is not the preferred procedure. Instead, a duodenoduodenostomy is often performed to connect the two ends of the duodenum, allowing normal passage of food from the stomach to the intestines.
Post-Surgical Outlook
With early surgical intervention, the prognosis for infants with duodenal atresia is generally positive. Post-operative care is crucial to ensure proper digestion and prevent complications such as infection or malabsorption.